Graphene Solid-state batteries represent the primary pathway for the future of battery technology, with graphene solid-state electrolytes serving as the essential technological components within the battery industry.
_看图王.png)
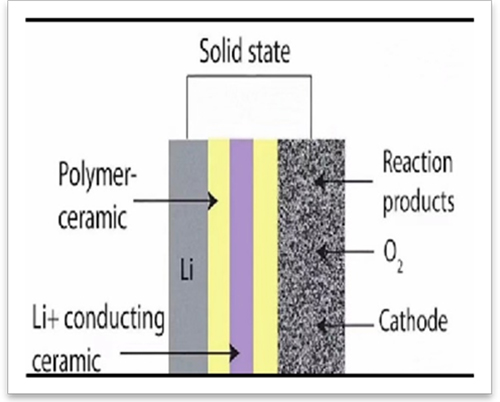
Graphene solid-state electrolytes consists of graphene sulfoselenide and features excellent safety performance, high energy density, high charging and discharging speed, light weight, high rate, long cycle life.
Self-development and production of advanced equipment and products and independent intellectual property rights of all products.
Solid-state electrolytes are materials used in batteries for discharge. Currently, there are three technological pathways for solid-state electrolytes in the market: polymers, oxides, and sulfides.
Graphene solid-state electrolytes is a colloidal electrolyte based on porous graphene as the substrate. This electrolyte boasts excellent safety performance, high energy density, reduced interfacial resistance, fast charge and discharge rates, lightweight and thin design, high rate capability, and long cycle life.

Cell test data summary table
Cell Type

EV
100Ah

EV
100Ah

EV
100Ah
Room Temperature (25°C)
Energy Density
| Low power C/20 | > 399 Wn/Kg | > 391 Wn/Kg | > 375 Wn/Kg |
| Low power C/10 | 399 Wn/Kg | (= 862 Wh at SOC 30%) | |
| Medium power C/3 | 390 Wn/Kg | 382 Wn/Kg | |
| Medium power 1C | 370 Wn/Kg | 363 Wn/Kg | 339 Wn/Kg |
| High power 3C | 351 Wn/Kg | 344 Wn/Kg | |
| High power 5C | 321 Wn/Kg |
Room Temperature (25°C)
Energy Density
| Low power C/20 | > 399 Wn/Kg | > 391 Wn/Kg | > 375 Wn/Kg |
| Low power C/10 | 399 Wn/Kg | (= 862 Wh at SOC 30%) | |
| Medium power C/3 | 390 Wn/Kg | 382 Wn/Kg | |
| Medium power 1C | 370 Wn/Kg | 363 Wn/Kg | 339 Wn/Kg |
| High power 3C | 351 Wn/Kg | 344 Wn/Kg | |
| High power 5C | 321 Wn/Kg |